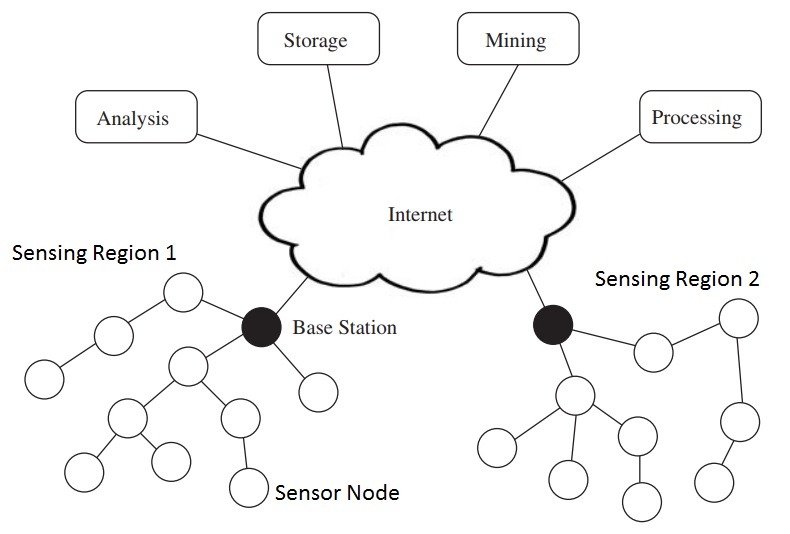
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are a type of network that consists of a large number of small, low-power devices called sensor nodes. These nodes are deployed in a physical area to collect data about the environment. The data is then transmitted to a central location, where it can be processed and analyzed.
WSNs are used in a wide variety of applications, including environmental monitoring, structural health monitoring, and industrial automation. However, WSNs can sometimes fail to work properly. There are a number of reasons why this might happen, including:
- Hardware failure: Sensor nodes are small and fragile devices, and they are susceptible to hardware failure. This can be caused by a number of factors, including environmental factors (such as extreme temperatures or humidity), physical damage, or software bugs.
- Software bugs: Software bugs can also cause WSNs to fail. This is especially true in complex WSNs that use sophisticated algorithms for data collection, processing, and transmission.
- Network congestion: WSNs can become congested if too much data is being transmitted at the same time. This can happen if the network is not properly designed or if there are too many sensor nodes in the network.
- Interference: WSNs can be susceptible to interference from other wireless devices, such as Wi-Fi networks or Bluetooth devices. This can cause data loss or errors.
- Security breaches: WSNs can be vulnerable to security breaches. This is because they often use wireless communication, which is a broadcast medium. This means that anyone within range of the network can potentially intercept data transmissions.
If you are experiencing problems with your WSN, there are a number of things you can do to troubleshoot the issue. Here are a few tips:
- Check the hardware: Make sure that all of the sensor nodes are properly connected and that they are not damaged.
- Update the software: Make sure that the software on all of the sensor nodes is up to date.
- Reconfigure the network: If the network is congested, you may need to reconfigure it to reduce the amount of data being transmitted.
- Use a different frequency: If the network is experiencing interference, you may need to use a different frequency for communication.
- Implement security measures: If you are concerned about security, you should implement security measures to protect the network.
If you have tried all of these things and you are still having problems, you may need to contact the manufacturer of your WSN for further assistance.
Here are some additional things you can do to prevent WSN problems:
- Design the network properly: When designing a WSN, it is important to consider the application and the environment in which the network will be deployed. This will help you to determine the number of sensor nodes needed, the type of hardware and software to use, and the best way to configure the network.
- Use high-quality components: Using high-quality components can help to reduce the risk of hardware failure.
- Perform regular maintenance: Regularly inspecting and maintaining your WSN can help to identify and correct problems before they cause a failure.
- Back up your data: Backing up your data regularly can help to minimize the impact of a failure.
By following these tips, you can help to ensure that your WSN is reliable and that it will continue to work properly for many years to come.